Arthrosis is a chronic joint disease in which the cartilage of the joint is progressively destroyed.As the cartilage is destroyed, changes arise in the bone that the cartilage covers and in the joint capsule. What does the word arthrosis mean and what synonyms are?
The term arthrosis comes from the Greek word "arthros" - the joint and suffix "Osis" - non -disabilities.However, this description is not entirely accurate, since with arthrosis in the joint there are some inflammatory changes.In the English -speaking countries, "our" arthrosis in the vast majority of cases is called arthritis (arthrithis), i.e.Inflammatory joint disease (ITIS suffix), while we are usually called arthritis, joint damage in rheumatic diseases, infectious, purulent damage to the joint, etc.Sometimes they try to correct this disagreement with another term: arthroso-arthritis, but it is rare.
In modern scientific articles, the term osteoarthritis is more often found (from the Greek words "osteo" - bone, "arthros" - joint, i.e. the non -inflammatory disease of the joint and bones).And again, in the English -speaking countries, “our” ostose arthrosis is called osteoarthritis (ostheoarthrithis), i.e.An inflammatory disease of the joint and bone.
Often from patients we hear the question: "At first they made me diagnosis arthrosis, and now osteoarthritis is already writing. Is it really so bad?"In fact, arthrosis and arthritis are synonyms, and your doctors talked about the same thing.
As we have already noted at the very beginning, with arthrosis (osteoarthrosis), the cartilage is progressively destroyed, and bones are gradually involved in the process.With arthrosis in the bone, a section of sclerosis (compaction) first occurs, as a result of loss of shock -absorbing properties.Then there are pointings along the edges of the bone (exostosis), which are often mistakenly called "
salts deposits " - in fact, with ordinary arthrosis there is no deposit of salts.In the further course of the disease, the bone begins to bend, deform, cysts are formed in it: often the disease is called deforming arthrosis (osteoarthrosis).In old medical books, you can sometimes find the phrase "disfiguring arthrosis", but now it is almost never used.
The exact causes of arthrosis were considered unknown for a long time, so there is another name for this disease - Idiopathic arthrosis , i.e.Arthrosis, which arose for unknown reasons or spontaneously.Of course, now scientists no longer consider arthrosis to a mystery and the reasons for its development are known.Read more about the causes of arthrosis, about what the primary and secondary arthrosis is below.
Arthrosis more often affects those joints that experience maximum loads (hip, knee, ankle joint, joints of the hand).Arthrosis of the hip joint is called COXARTHROSIS (from the word "COXA" - hip), the ankle joint - CRUROSTEOOARTHRITIS ("CRURIS" - lower leg), knee - gonarthrosis ("Gene" - knee).In most cases, arthrosis affects both knee joints, while one of the joints can be more destroyed.In this case, the diagnosis sounds like a bilateral gonarthrosis with a predominant damage to the right (or left) knee joint.
Often, arthrosis is affected not by one, but several joints, so they use another term - Polyosostoarthritis which means damage to three or more joints (two symmetrical, for example, both of the knee, and some other).In this case, the diagnosis usually sounds as follows: Polyosteoarthrosis with a predominant damage to the knee joints (or one of them).
Why does arthrosis of the knee joint occur?
Arthrosis of the knee joint can be different.Depending on the causes of its occurrence, primary and secondary arthrosis is distinguished.
Primary arthrosis of the knee joint
joint cartilage is constantly destroyed and updated, and normally these processes are balanced.With age, the update of the cartilage slows down and the destruction of the cartilage, which is called the process of degradation or degeneration, begins and begins to prevail.
The process of synthesis and destruction of cartilage is normally balanced.If degeneration begins to prevail, then the arthrosis of the knee joint will begin
In most cases, the degeneration of cartilage, that is, the development of arthrosis, occurs after 45-50 years, but sometimes arthrosis can develop in 20 years.Fortunately, the development of arthrosis at such a young age is extremely rare.

People are prone to arthrosis of the knee joint to a greater or lesser extent.As a rule, if arthrosis occurs, then just at the age of 40-60 years, and if by the age of 60 there is no arthrosis, then most likely it will no longer be, or, more precisely, arthrosis will be insignificant (certain degenerative changes in the knee joint are found in all elderly people, but they are expressed differently).
It is important to note that if you take radiographs to all older people.For example, 60 years, then almost 90%will be signs of arthrosis, but not all of them feel their knees as problematic.This is especially true for men who often already “serious” arthrosis does not show itself or causes minimal inconvenience.
Primary arthrosis occurs spontaneously, i.e.Without launching factors, therefore it is called idiopathic, which we talked about earlier.
So, we have already found out that age is one of the main factors that determine the development of arthrosis, since the processes of cartilage degeneration begin to prevail with age.Every fourth person over 55 years old suffers from arthrosis of the knee joints.But we also noted that with age, arthrosis does not develop in everyone.So there are other reasons.Before we list them, we note that there is no main, main reason.The arthrosis of the knee joint develops in terms of causes, while some play a large role, while others - smaller.
Floor. Often, arthrosis of the knee joint suffers from women.The exact reasons for this are unknown, but you can try to explain the following reasons.On average, the life expectancy of women is greater than in men, and, accordingly, the average elderly woman will more express degenerative processes.In addition, the body weight in women is on average slightly higher.The size of the bone in women is smaller than in men, and, coupled with a higher body weight, this leads to a higher pressure in the knee joint, and, accordingly, more intense mechanical destruction of cartilage.In the overwhelming majority of cases in women, arthrosis begins to appear after the cessation of menstruation, and, possibly, the deficiency of estrogens determines the development of arthrosis.Note that attempts to treat arthrosis of the knee joint in women after menopause by estrogens are, of course, undertaken, but so far they are unsuccessful.
Weight. Of course, the more body weight, the greater the load has to be transferred to our knee joints.In addition, overweight reduces physical activity and leads to the weakness of the hip muscles.For a more active synthesis of cartilage, movements (without excess pressure) are necessary, and with a sedentary lifestyle, the processes of cartridge of cartilage begin to prevail.The hip muscles are important stabilizers of the knee joint, and with the weakness of these muscles, the movement in the knee joint becomes more painted, which accelerates the destruction of cartilage.In general, these processes can be described as a vicious circle: the more body weight, the faster the knee joint is destroyed, the more pain, the more difficult to move, which again leads to overweight.

The vicious circle of obesity and arthrosis of the knee joint
On the other hand, it is not necessary at all that arthrosis of the knee joint develops only among complete people - those who do not have any obesity can also suffer from arthrosis.Again, this is because arthrosis has no one reason.
Heredity. It has long been noticed that arthrosis of the knee joints is a "family" disease.If you have arthrosis or your parents, then, unfortunately, the probability of this disease is high with you.Scientists have discovered many gene features that are responsible for, for example, the individual features of the structure of the main cartridge of the cartilage - collagen, but, unfortunately, so far these discoveries have no practical significance, because we can not affect the prevention or treatment of arthrosis.There is evidence that the inheritance of arthrosis is transmitted along the female line, which partially explains their great tendency to this disease.
Primary arthrosis of the knee joint does not occur only for one reason, but only by their aggregate.At the same time, arthrosis of the knee joint is to one degree or another in almost all people over 60, but the severity of arthrosis is very different, and not always arthrosis found on radiography manifests itself.In fact, it is even more difficult: not any pain in the knee joint in an elderly person or, moreover, at the age of 40-60 years will be accompanied by changes in the radiograph characteristic of arthrosis.
For example, scientists have found that 76% of the elderly with complaints of pain in the knees on the radiograph is found arthrosis. That is, not any pain in the knee joint of an elderly person is necessarily arthrosis of the knee joint. At the same time, among all the elderly people with arthrosis of the knee joints found on the radiograph, only 81% will make complaints about pain. That is, not always existing arthrosis hurts.
Strictly speaking, there is no obligatory connection of the severity of pain with the severity of arthrosis of the knee joint on the radiograph.It happens that the changes on the radiograph are completely insignificant, and the pain is strong, and it happens the other way around: the joint is completely destroyed on the X -ray, and a person can ride a bicycle, engage in yoga, work as a malarus, and such cases are found almost every day.
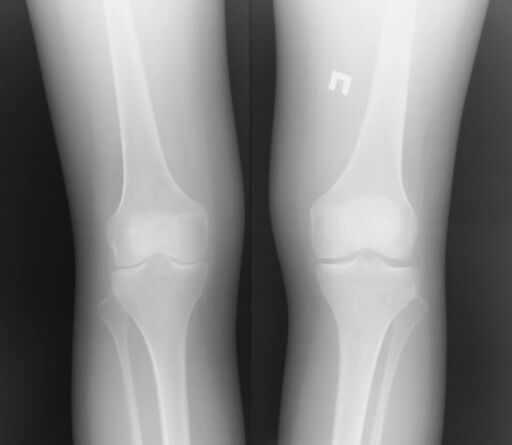
More often arthrosis of the knee joint begins with the internal (medial) department.
Randigns of the knee joint, affected by arthrosis withthe inside.The blue arrow marked the outer section of the joint, and the orange - the interior of the joint.Pay attention to how already the gap between the bones is from the inside: the cartilage is not visible on the radiograph, and it is this gap that means cartilage.In this case, there is practically no cartilage left on the inside of the knee joint and the bone is already rubbed on the bone.
With gradual abrasion of the cartilage, the leg begins to bend from the inside of the knee joint.Since arthrosis often affects both knee joints, that is, it is bilateral, both legs begin to be curved, and an O-shaped legs deformation (varior deformation) occurs.
Less often (in about 10% of cases), the external joints of the joint are affected, and in this case, X-shaped (valgus) deformation begins.
Of course, with curvature, the load on the internal (with O-shaped) or external (with x-shaped) deformation variants increases even more, and arthrosis will develop faster and irrevocably.
Arthrosis can begin not only in the internal or external section, but also between the knee cup (chilling) and the inter-crib furrow of the femoral.This option is called patello-femory arthrosis and it occurs, as a rule, due to tilt, subluxation of the patella, lateral hyperpression syndrome which is devoted to a separate article on our website or after fractures of the patella , which you can also read about in a separate article.
Secondary arthrosis of the knee joint
Arthrosis of the knee joint can also develop due to any specific causes, in this case arthrosis is called secondary.Now we will briefly talk about the options for secondary arthrosis.
Post -traumatic arthrosis of the knee joint. Injuries of the knee joint, of course, do not add a joint of health and almost all of them, one way or another, increase the risk of arthrosis.
One of the most common injuries of the knee joint - ruptures of meniscus, which is devoted to a separate article on our website.Unfortunately, any person with the gap of meniscus has ever had the likelihood of developing arthrosis ever.If a medial (internal) meniscus is damaged, then arthrosis will rather develop in the interior of the knee joint.And, accordingly, if the external meniscus bursts, then arthrosis will develop in the outer joint of the joint.Note that the rupture of the meniscus does not always necessarily lead to arthrosis, the probability of its development auls.Of course, the more the meniscus is damaged, the higher the risk of arthrosis.
Another reason for the development of arthrosis of the knee joint is ruptures of the ligaments, for example, a rupture of the front cruciate ligament.As a result of the rupture of the ligament in the joint, instability may appear, which, of course, will lead to damage to the cartilage and the development of arthrosis.Naturally, the damage to the cartilage depends on the degree of instability, which can be different.
Much more severe trauma of the knee joint - a fracture of the tibia tires or a fracture of the femoral buttonholes if the fracture line enters the articular surface, then such a fracture is called intraarticular.Almost any intra -articular fracture is accompanied by a displacement of fragments, and thus, the shape of the articular surface changes.The step that appears as a result of the shift inevitably leads to progressive destruction of cartilage and the appearance of arthrosis.Of course, the heavier a fracture, the larger the intraarticular fracture of the fragments, the more the cartilage is damaged and the risk of arthrosis is higher.After heavy multi -horned fractures of tumbling condyles, arthrosis develops in almost 100% of cases even despite the perfectly performed osteosynthesis operation (elimination of bone fragments and fastening with screws, plates, etc.)
















































